If youāve been grocery shopping recently, youāve seen the signs: flyers at all check-outs urgently requesting donations for Feed Nova Scotia after the organization announced theyāre critically low on food.
As the community stepped up to help, including Dalhousie with its donation of over a tonne of food, the situation at Feed Nova Scotia prompts a larger question: how food secure are our populations?
Well, 8.3 per cent of Canadians are food insecure ā an issue one group on campus is looking to tackle at its roots.
is a four-week long summer enrichment program for exceptional high school students. Each year over 600 students gather at 12 universities campuses across Canada, including at pilipiliĀž». During their month-long stay on campus, students work in teams, combining science, technology, engineering, arts and math (STEAM) skills with entrepreneurial innovation to create a product that will help solve one of the worldās big issues. This year the focus is on food security.
Exploring issues
Nicholas Barclay is one of this yearās Dal participants. The 17-year-old from Victoria, B.C., came to Dal to experience the east coast and explore his interest in engineering. Though science-focused, he said heās enjoying the diversity that the āintenseā program has to offer.

āItās not just about not having enough food,ā Nick explains, adding that he and his peers were aware of food insecurity issues, but not the specifics. āThereās malnutrition, lack of accessāyou have to consider all the different facets.ā
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, food security is defined as having access to enough food to lead a healthy active life. The food also has to be culturally appropriate. Ā
, assistant professor with the Marine Affairs Program and the Canadian Research Chair in Integrated Ocean and Coastal Governance, introduced this yearās topic to the group. She was impressed with the level of knowledge the students already had.
āThey brought up people with disabilities, people with poor mental health, the elderly ā thereās a wide range of people who might face challenges,ā says Dr. Bailey.

As part of the introductory lecture, the group looked at a case study of the Arctic, where entire communities face particularly challenging food security issues. High fuel prices mean higher shipping costs. There are longer shipping times and with longer, warmer winters, the chance of food spoilage is increased. Arctic communities also face the limiting of their traditional food sources: āMost of us, weāre not hunters or fishermen, we shouldnāt be imposing our standards on people who are culturally different,ā says Nicholas.
The case study also allowed students to look at an aspect of food security that often goes overlooked: malnutrition. Some people may have access to food, but that food doesnāt have a high enough nutritional value. To learn about the work required to produce healthy food, students visited the Common Roots Urban Farm near the QEII hospital in Halifax. While there, they split into groups to make compost, weed the āfood forestā and do maintenance on the pathways and signs.
āBeing able to see where food actually comes from is really important. Thatās why we go out and help with the garden and visit a dairy farm,ā says , a SHAD co-director and associate professor in the School of Information Management. āThey not only contribute to the local community, but it helps them understand the process of getting food from farm to table and get a feel for the complex and moving parts.ā
Innovative ideas
Understanding where food comes from is the premise of Nicholasā groupās project: a gardening system for young children.
Itās the groupās hope that the system will connect people at an early age to the process of food production, and increase their ability to make healthier choices in the future. āThe difficulty is creating something that is fun and interesting for kids, while being accessible and easy to use,ā he explained. āIt also needs to be something parents are willing to buy for their kids.ā
The group might be on the right track.
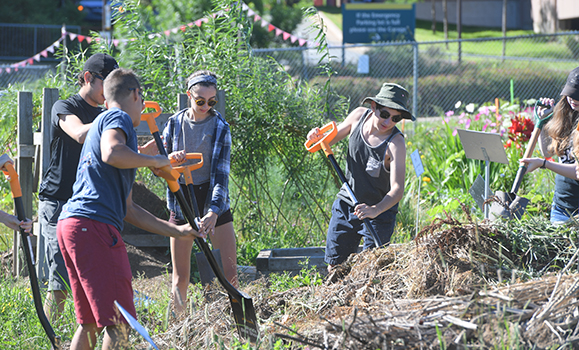
āThe young have to have a voice in the future weāre creating,ā says Dr. Bailey, who recently co-edited a special edition of Solutions. The journal features thoughtful articles on food-security solutions. For the special edition, Dr. Bailey and co-editor Jessica Duncan sought out contributions exclusively written by young academics around the world.
āThis is one of the consequences we saw with Brexit,ā she continues. āThe older population voted to leave, while the younger population voted to stay. Itās the older generation making choices with consequences that the younger generation is going to have to live with. High schoolers or young academics should be creating their own vision of a sustainable food future.ā
Creating that vision wonāt be easy, says Nicholas. āThereās a lot to consider. Do you focus on production, understanding, nutrition, or waste? For example, 20 per cent of food is wasted before it even gets to the retailers because it has to look a specific way. Changing perception is going to be one of the biggest challenges.ā
However, Nicholas agrees that the young are best suited for the job. āWe have no filters,ā he says. āWe havenāt learned how to shut down our own ideas.ā
Carrying it through
SHAD aims to make sure they never do. Dr. Smit has been with SHAD since his undergrad days. According to his experience, SHAD helps students figure out how to move beyond where they are now, to broaden their horizons, and offers opportunities that help them explore new ideas. āWeāre equipping Canadaās future leaders to be ready.ā
Though the task may be daunting, Nicholas feels he and his peers are prepared. āWeāre being handed the world we live in. Weāll be the ones to carry it on and see it through.ā

